Osteochondrosis is a long-term disease. Most often, when assessing the severity of pathological processes, four stages are distinguished:
- The first stage is the period of initial changes occurring in the fibrous ring of the disc, which the patient often does not even notice;
- The second stage corresponds to the appearance of instability in the affected segment of the spine, a decrease in the height of the disc;
- The third stage is characterized by the appearance of hernias or osteochondral growths - osteophytes; the fibrous ring is almost destroyed at this stage;
- The fourth stage is characterized by irreversible damage to all structures providing intervertebral articulation, disc fibrosis and loss of mobility of the affected segment.
Causes of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
It has been shown that from the age of about 20, our vertebrae slowly deteriorate. As we age, wear and tear on the spine progresses. Degenerative processes decrease the thickness of the intervertebral disc, which acts as a shock absorber. In addition, pathological structures appear on the bony edges of adjacent vertebrae: bone spurs, spondylophytes, which reduce the range of motion.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes begin in the nucleus pulposus and then spread to the annulus fibrosus and other structural elements of the vertebra, causing the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
Due to the loss of water, the nucleus pulposus ceases to evenly distribute the vertical load. This negatively affects the annulus fibrosus. Excessive compaction (compression) leads to mechanical damage, the appearance of tears and cracks. The joints begin to be overstressed, which gradually leads to spinal instability and pain.
Thus, the main cause of osteochondrosis is natural aging. However, its development is facilitated by the combined effect of several unfavorable factors that increase the probability of the disease's manifestation. These include:
- Smoking;
- He performed surgical interventions on the spine;
- Injuries to this part of the spine;
- Curvature of the spine (scoliosis);
- Weakness of the back muscles;
- Excess body weight;
- Increased load on the spine.
It is assumed that the involution (aging) of the cartilage and bone tissue of the vertebrae is genetically determined, and the progression to the disease state with characteristic symptoms and manifestations occurs as a result of external and internal factors. The processes can start even earlier if damage (mechanical, inflammatory, etc. ) precedes them.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the chest region
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine depend on the stage of the pathological process and existing structural abnormalities. Unlike other areas of the spine (cervical, lumbar), radicular syndrome and other neurological complications are less common in the thoracic region. This is explained by the presence of the thoracic skeleton, which limits the displacement and compression of this part of the spinal column. Most often, pain in the chest region (dorsalgia or thoracic lumbago) is associated with immobilization of the intervertebral joints.
Reference! Thoracic lumbago or dorsago in neurology refers to acute pain of high intensity that occurs in the thoracic spine, often associated with difficulty breathing. The cause of the condition lies in a severe spasm of the back muscles. It cannot be ignored because. . . Similarly, a heart attack can begin, and frequent lumbago can be associated with serious pathologies in the body.
The pain can last from several hours to several days. It is usually not as intense as damage to other parts of the spine, but it is also related to movement of the spinal column. In addition, muscle hypertonia is noted in this area, which can be combined with weakness and numbness of the hands.
The pain can be dull, burning, deep, paroxysmal or constant. It can be felt in the chest, heart and other organs. Patients describe it as a "stake in the chest, " a "ring of the chest, " a "knife between the shoulder blades. " This phase is characterized by radiating and circling pain with deep sighs, coughing, and sudden chest movements.
Without treatment, osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is often complicated by intercostal neuralgia. In this case, the burning pain may be localized in the region of the heart, and the patient may mistake it for manifestations of cardiac pathology.
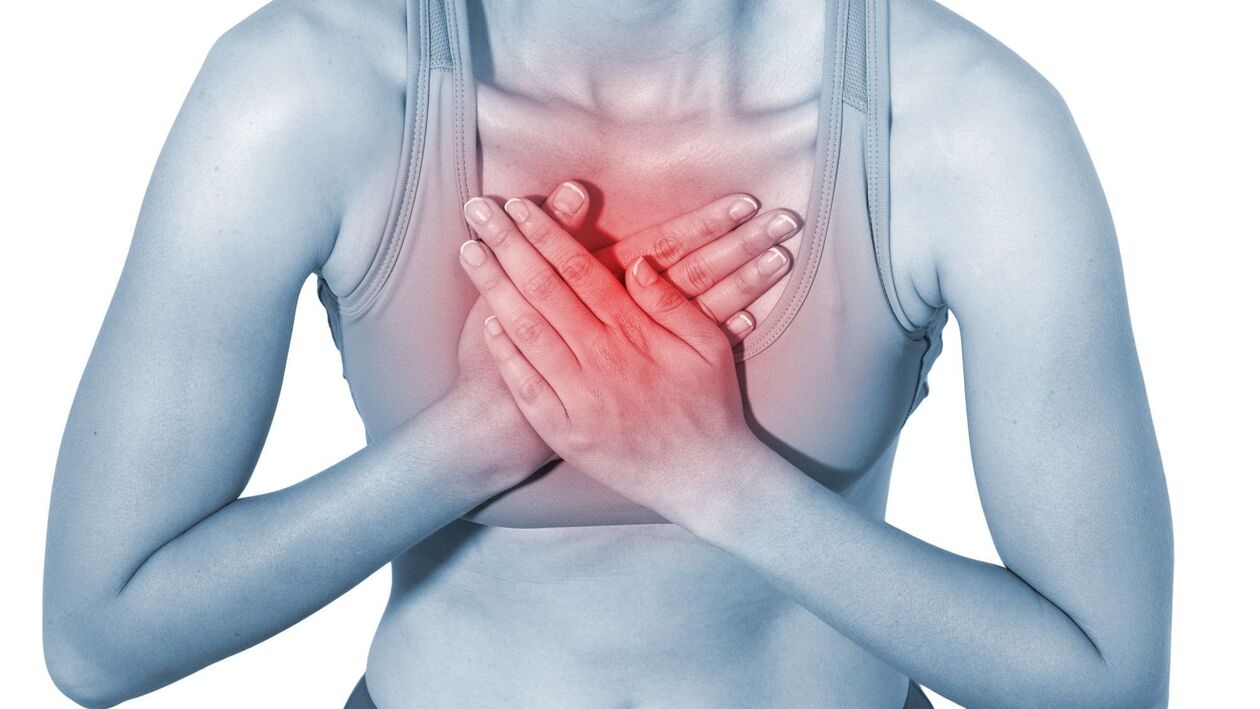
Important! If you feel pain in the area of the heart, do not try to make a differential diagnosis on your own. In order to rule out heart diseases and prevent the progression of pathological processes in the spine, it is important not to delay seeing a doctor, not to wait for pain and not to self-medicate.
The pain may increase with physical activity, bending and psycho-emotional stress. If the outer vertebrae of this area are affected, the pain can radiate to the lower back, sacrum, and even the buttocks.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
Diagnosing osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is a multi-step process. First, the doctor collects an anamnesis:
- Know your medical history;
- Have you had any close relatives with spinal disease?
- How long ago did the symptoms start and how intense are they;
- What are the accompanying diseases?
A physical examination of the patient is required, including examination of the skin, assessment of postural abnormalities, and palpation (palpation) of the muscles near the spine. Neurological tests can be performed to establish the diagnosis.
Instrumental diagnostics
Imaging diagnostics make it possible to assess the degree of cartilage damage, identify other existing disorders and rule out diseases with similar symptoms. The recommended methods for the instrumental diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine are as follows:
- X-ray (spondylography) - provides information on the structure of the bone, the presence of osteophytes, the state of the facet joints;
- CT (computed tomography) allows you to examine everything in detail and take measurements if necessary; it has advantages over MRI in the diagnosis of pathology of bone structures;
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) makes it possible to assess the condition of soft tissues, diagnose inflammatory processes, tumors, spinal hernia, identify pathological changes in cartilage, bones, ligaments, blood vessels, and determine the narrowing of the spinal canal. With the help of MRI, vascular pathologies and tissue circulation disorders are detected in the thoracic spine.
Medicinal blockades can also be used for diagnostic purposes. Due to the diversity of pain manifestations, further research is often needed to rule out:
- Angina pectoris;
- Myocardial infarction;
- Aortic aneurysms,
- Cholecystitis,
- Peptic ulcer;
- Pneumonia;
- Oncological diseases, etc.
Methods of treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis

Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is a disease that requires complex treatment. In addition to pain-relieving drug treatment, it is important to contact trauma and neurological specialists in order to reveal the exact causes of disturbing symptoms.
Treatment tactics depend on the severity of the disease. Conservative therapy, such as physical therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, heat therapy, and nerve block injections, is usually the first treatment option.
Practical therapy for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region allows strengthening the muscles of the back and interscapular region, forming muscle ligaments and correct posture, muscle relaxation and improving blood circulation in this segment of the spine. In osteochondrosis of this area, breathing exercises, joining the shoulder blades and rotating the shoulders are useful.
The massage helps to normalize blood supply, lymphatic drainage, and activates metabolic processes. It is prescribed outside of an exacerbation, when the patient does not suffer from severe pain. Various types of therapeutic massage are used: manual (manual), underwater, vacuum massage.
Manual therapy methods are also popular. Chiropractors work with blocks and clamps in the musculoskeletal system, removing them using various techniques. In case of acute pain, acupressure or acupressure can be performed. In doing so, the doctor exerts a therapeutic effect on the entire body by pressing his fingers at certain points with different intensities.
Physiotherapy techniques are quite effective in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine. They help reduce pain, improve blood circulation and strengthen the muscles of the spine. Among them:
- Ultrasound therapy;
- electrophoresis of drugs;
- Laser therapy in the area of the spine;
- Transcutaneous electrical neuromyostimulation;
- Exposure to magnetic fields;
- Electrical impulse therapy.
In order to enhance the therapeutic effect, a combination of medicinal and non-medicinal therapeutic methods is recommended. Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine may take a long time, but the results will be visible after the first procedures. The most important thing is not to delay the visit to the doctor and not to start treatment in the early stages of the disease.
If conservative treatment does not help, surgery may be necessary. Most often, decompression and stabilization operations are performed. They make it possible to stop compression of the spinal cord, nerve roots by hernias, osteophytes or hypertrophic ligaments and fix the affected segment.
After the surgical treatment, you will need to wear a special brace for a while. Upon leaving the hospital, a medical rehabilitation course is prescribed.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis at home
Home treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine can be effective if several conditions are met. First of all, the diagnosis must be made by a specialist after a complete examination. Treatment methods should also be discussed with a doctor to make sure that there are no contraindications in the presence of concomitant pathologies.
The most important and fundamental thing is to maintain a healthy lifestyle, control your body weight and add adequate physical activity. The best way to treat back pain is exercise. They help to strengthen the back muscles, improve blood circulation, cope with stress more easily, and thus prevent the progression of the disease.
If the condition worsens or there is a strong, sharp pain, it is better to lie down and make sure that the spine remains at rest. Heat treatments and massage help to cope with discomfort. In any case, home treatment does not replace consultation with a specialist and the implementation of his recommendations. Uncontrolled self-medication can lead to deterioration of the condition and the development of complications.
Which doctor should I see?
Neurologists and orthopedists treat osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine. They diagnose, make a diagnosis and choose the appropriate treatment. Patients may need to see a physiotherapist and exercise therapy doctor.
If you have pain in the chest region, you can also consult a therapist. He analyzes the clinical manifestations, prescribes the necessary tests and refers him to a specialist.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
The doctors of the regional clinic help to cope with the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine. In most clinics, almost all clinics have the necessary modern diagnostic equipment, which allows obtaining the most accurate information about the condition of the spine and choosing the most effective treatment method. Experienced specialists of various profiles help patients restore their health in comfortable conditions: neurologists, orthopedists, physiotherapists, masseurs, therapists.
If necessary, in modern reality, you can ask for advice from other specialists in the shortest possible time and without queues. The consultants are ready to help you if you have any questions. Fill out the feedback form online and they will surely call you back.